Streptomyces
Материал из Поле цифровой дидактики
| Описание микроба | Streptomycetes are the most widely studied and well known genus of the actinomycete family. Streptomycetes usually inhabit soil and are important decomposers. They also produce more than half of the world's antibiotics, and are consequently invaluable in the medical field. |
|---|---|
| Верхний таксон | Bacteria; Actinobacteria; Actinobacteridae; Actinomycetales; Streptomycineae; Streptomycetaceae. |
| Species - виды | Streptomyces coelicolor, S. lividans, S. albicans, S. griseus, S. plicatosporus |
| Genome Structure= структура генома | The entire genome of Streptomyces coelicolor was sequenced as of July 2001. The linear chromosome is 8,667,507 bp long and is predicted to contain 7,825 genes, about twice as many as typical free-living bacteria, making it the largest bacterial genome yet sequenced. The linear chromosome replicates from a central origin. The single chromosome also has a unique telomere structure. During replication the 5' end of the chromosome remains incomplete, resulting in a single strand of DNA at each end. The single strands have several replicating sequences that double over to form hairpin structures at either end of the chromosome, forming protective telomeres (Goshi et al.). Streptomyces avermitilis was also been sequenced in October 2001. It is 9,025,608 bp long, and has 7,575 ORFs assigned. This organism is a well known producer of the anti-parasitic agent avermectin which is widely used to rid livestock of worm and insect infestations and to protect large numbers of people from river blindness in sub-Saharan Africa. There are also two genome projects in the works for Streptomyces scabiei and Streptomyces ambofaciens |
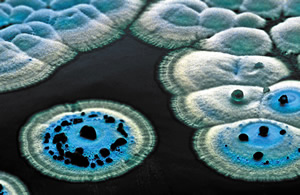
| Cell Structure - клеточная структура | Streptomycetes resemble fungi in their structure. Their branching, filamentous arrangement of cells form a network called a mycelium. They are able to metabolize many different compounds including sugars, alcohols, amino acids, and aromatic compounds by producing extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. Their metabolic diversity is due to their extremely large genome which has hundreds of transcription factors that control gene expression, allowing them to respond to specific needs. |
| Ecology= экология обитания | Streptomycetes are found worldwide in soil, and are largely responsible, through the secretion of chemicals called geosmens, for the earthy smell of soil. streptomycetes consequently play an important role in the degradation of organic matter, most commonly noted in compost piles.
Several species of Streptomyces are involved in a symbiotic relationship with species of ants in the genus Attini. Attine ants cultivate fungus in, what are termed fungal gardens. They perform all the motions of human farmers, weeding, and nurturing their gardens. The small bacterium in the streptomyces genus inhabits the cuticles of the ants, and aids in weeding their fungal gardens. Streptomycetes produce toxins that keep the main weed in ant fungal gardens, another fungi, Escovopsis, at bay. |
https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Streptomyces