Micrococcus: различия между версиями
Материал из Поле цифровой дидактики
Patarakin (обсуждение | вклад) Новая страница: «{{Microbs |Description=M. luteus can be found in many places such as the human skin, water, dust, and soil. Micrococcus was first isolated by Alexander Fleming in 1929, as Micrococcus lysodeikticus before it was known as micrococcus luetus (Ganz et al, 2002) Micrococcus is generally thought of as harmless bacterium, but there have been rare cases of Micrococcus infections in people with compromised immune systems, as occurs with HIV patients. M. lutues can b...» |
Patarakin (обсуждение | вклад) Нет описания правки |
||
| Строка 1: | Строка 1: | ||
{{Microbs | {{Microbs | ||
|Description=M. luteus can be found in many places such as the human skin, water, dust, and soil. Micrococcus was first isolated by Alexander Fleming in 1929, as Micrococcus lysodeikticus before it was known as micrococcus luetus | |Description=M. luteus can be found in many places such as the human skin, water, dust, and soil. Micrococcus was first isolated by Alexander Fleming in 1929, as Micrococcus lysodeikticus before it was known as micrococcus luetus Micrococcus is generally thought of as harmless bacterium, but there have been rare cases of Micrococcus infections in people with compromised immune systems, as occurs with HIV patients. M. lutues can be mistaken for S. aureus. The two species share similar colony morphology as well as a similar yellow colony color. To distinguish between the two, a bacitracin test may be performed. M. lutues does not grow in the presence of bacitracin, and will leave a clear ring with no growth on the dish around the bacitracin disk. M. luteus is unique in its ability to absorb UV radiation. It has pigments that absorb long wave UV radiation, between 350-475 nanometer | ||
|Higher order taxa=Bacteria; Actinobacteria; Actinobacteria (class); Actinobacteridae; Actinomycetales; Micrococcineae; Micrococcaceae | |Higher order taxa=Bacteria; Actinobacteria; Actinobacteria (class); Actinobacteridae; Actinomycetales; Micrococcineae; Micrococcaceae | ||
|Species=Micrococcus antarcticus; M. luteus; M. lylae; M. roseus; M. agilis; M. kristinae; M.sedentarius; M. halobius; M. sp. | |Species=Micrococcus antarcticus; M. luteus; M. lylae; M. roseus; M. agilis; M. kristinae; M.sedentarius; M. halobius; M. sp. | ||
Версия от 19:37, 22 сентября 2022
<vote type=1 />
| Описание микроба | M. luteus can be found in many places such as the human skin, water, dust, and soil. Micrococcus was first isolated by Alexander Fleming in 1929, as Micrococcus lysodeikticus before it was known as micrococcus luetus Micrococcus is generally thought of as harmless bacterium, but there have been rare cases of Micrococcus infections in people with compromised immune systems, as occurs with HIV patients. M. lutues can be mistaken for S. aureus. The two species share similar colony morphology as well as a similar yellow colony color. To distinguish between the two, a bacitracin test may be performed. M. lutues does not grow in the presence of bacitracin, and will leave a clear ring with no growth on the dish around the bacitracin disk. M. luteus is unique in its ability to absorb UV radiation. It has pigments that absorb long wave UV radiation, between 350-475 nanometer |
|---|---|
| Верхний таксон | Bacteria; Actinobacteria; Actinobacteria (class); Actinobacteridae; Actinomycetales; Micrococcineae; Micrococcaceae |
| Species - виды | Micrococcus antarcticus; M. luteus; M. lylae; M. roseus; M. agilis; M. kristinae; M.sedentarius; M. halobius; M. sp. |
| Genome Structure= структура генома | M. luteus has one of the smallest genomes of all bacteria. Hybridization studies show no close genetic relationship among the species of Micrococcus. For example, M. luteus and M. lylae are 40-50% genetically different. M. luteus has a G-C content of 65-75 mol%. M. varians has a G-C content of 66-72mol%. About half of the strains of M. luteus were found to carry plasmids 1 to 100MDa in size. So far two genome sequences have been done, one on Micrococcus sp. 28 plasmid pSD10 and another on Micrococcus luteus plasmid pMLU1. |
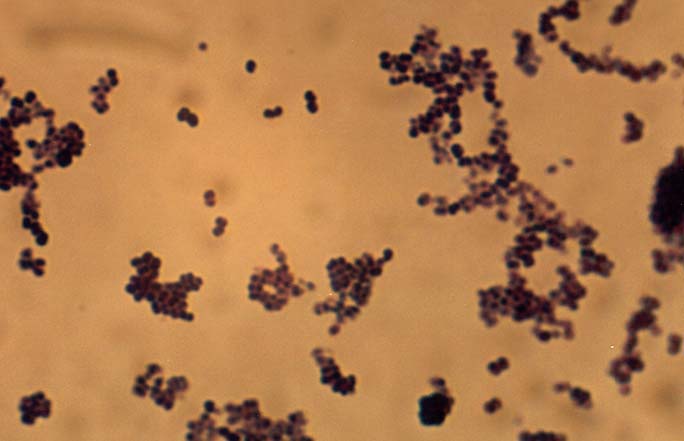
| Cell Structure - клеточная структура | Micrococcus are Gram-positive cocci that are 0.5 to 3.5 micrometers in diameter and usually arranged in tetrads or irregular clusters. They are generally strict aerobes and can generally reduce nitrate. M. luteus oxidizes carbohydrates to CO2 and water, and it does not produce acid from glucose as well as it does not make arginine dihydrolase or b-galactosidase. Some Micrococcus are pigmented bacteria; for example, M. luteus produces yellow colonies and M. roseus produces redish colonies. Micrococcus species are oxidase-positive, which can be used to distinguish them from other bacteria like most Staphylococcus species, which are generally oxidase-negative.Micrococcus species can also be differentiated from staphylococcus species by the Taxo A Bacitracin disk test |
| Ecology= экология обитания | M. luteus has been isolated from human skin, animal and dairy products, and beer. It can be found in many other places in the environment, as well, like water, dust, and soil. M. luteus on human skin breaks down compounds in sweat into compounds with bad odor. M. luteus can grow well in environments with little water or high salt concentrations. M. varians is the second most frequently isolated species of micrococcus after Micrococcus luteus |
https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Micrococcus